老年吸入性肺炎患者预后的影响因素论文
2023-12-11 15:25:06 来源: 作者:hemenglin
摘要: 目的:分析老年吸入性肺炎(AP)患者预后的影响因素。 方法: 选取 2022 年 9 月至 2023 年 3 月该院收治的 150 例老年 AP 患者进行横断面研究
【摘要】 目的:分析老年吸入性肺炎(AP)患者预后的影响因素。 方法: 选取 2022 年 9 月至 2023 年 3 月该院收治的 150 例老年 AP 患者进行横断面研究,收集其一般资料,观察其预后不良发生率, 比较不同预后患者一般资料,采用多因素 Logistic 回归分析老年 AP 患者预后的影响因素。结果: 150 例老年 AP 患者预后不良 41 例,占 27.33%(41/150)。预后不良患者急性生理学与慢性健康状况评分系 统Ⅱ(APACHE Ⅱ)评分、血清超敏 C 反应蛋白(hs-CRP)水平、血清血管生成素 -2(Ang-2)水平均高于预后良好患者,差异有统计 学意义(P<0.05) ;不同预后患者的性别、年龄、体质量指数、糖尿病占比、高血压占比、心脑血管疾病占比、帕金森病占比、鼻饲占比、 淋巴细胞计数、中性粒细胞比例、血红蛋白水平、总胆固醇水平、三酰甘油水平、空腹血糖水平、平均动脉压比较,差异无统计学意义 ( P>0.05) 。多因素 Logistic 回归分析结果显示, APACHE Ⅱ评分 >17.15 分、血清 hs-CRP>54.13 mg/L、血清 Ang-2>12.33 μmol/L 均为老年 AP 患者预后不良的危险因素(OR>1. P<0.05)。 结论: APACHE Ⅱ评分 >17.15 分、血清 hs-CRP>54.13 mg/L、血清 Ang-2>12.33 μmol/L 均为老年 AP 患者预后不良的危险因素。
【关键词】 老年,吸入性肺炎,预后,影响因素
Influencing factors ofprognosis in elderly patients with aspiration pneumonia
ZHAO Qian
(Department of Geriatrics of the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanyang Medical College, Nanyang 473000 Henan, China)
【 Abstract】 Objective:To analyze influencing factors of prognosis in elderly patients with aspiration pneumonia (AP). Methods:A cross-sectional study was conducted on 150 elderly patients with AP admitted to the hospital from September 2022 to March 2023. Their general information was collected. The incidence of poor prognosis was observed. The general data of these patients with different prognosis were compared. Multivariate Logistic regression analysis was used to analyze the influencing factors of prognosis in the elderly patients with AP. Results:Among the 150 elderly AP patients, 41 had poor prognosis, accounting for 27.33% (41/150). The acute physiology and chronic health status scoring system II (APACHE II) scores, the serum hypersensitive C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) levels, and the serum angiopoietin-2 (Ang-2) levels of the patients with poor prognosis were higher than those of the patients with good prognosis, and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). There were no significant differences in gender, age, body mass index, proportion of diabetes, proportion of hypertension, proportion of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, proportion of Parkinson’s disease, proportion of nasal feeding, lymphocyte count, proportion of neutrophils, hemoglobin level, total cholesterol level, triacylglycerol level, fasting blood glucose level and mean arterial pressure among the patients with different prognosis (P>0.05). The multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that APACHE II score >17.15. serum hs-CRP >54.13 mg/L, and serum Ang-2 >12.33 μmol/L were all risk factors for poor prognosis in the elderly AP patients (OR>1. P<0.05). Conclusions:APACHE II score >17.15. serum hs-CRP >54.13 mg/L, serum Ang-2 >12.33 μmol/L are the risk factors of poor prognosis in the elderly AP patients.
【Keywords】 Elderly; Aspiration pneumonia; Prognosis; Influencing factor
吸入性肺炎(AP)指吸入异物或口腔分泌物 进入下呼吸道而引起的肺炎,严重者可发生呼吸衰 竭、呼吸窘迫综合征 [1-2] 。老年人群呼吸系统结构 和功能减退,易患 AP[3] 。老年 AP 病程较长,病死 率较高 [4] 。本文分析老年 AP 患者预后的影响因素。 1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 选取 2022 年 9 月至 2023 年 3 月 本院收治的 150 例老年 AP 患者进行横断面研究。 纳入标准:符合 AP 诊断标准 [5] ;年龄≥ 60 岁。排除标准:合并其他呼吸系统疾病;具有免疫系统疾 病或使用免疫抑制剂;合并认知障碍或精神障碍 而无法配合研究;临床资料不完整;伴血液系统病 变。患者及家属对本研究内容了解且自愿签署知情 同意书,研究经本院伦理委员会审批通过。150 例 老年 AP 患者中, 男 81 例, 女 69 例; 年龄 60~68 岁, 平均(63.19±2.07) 岁; 体质量指数(BMI) 17.50~29.10 kg/m2 , 平 均(23.34±2.80)kg/m2 ;合 并糖尿病 34 例,高血压 66 例。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 资料收集 自制《一般资料调查问卷》,内 容包括性别、年龄、BMI、糖尿病(有、无) 、高血压(有、无) 、心脑血管疾病(有、无) 、帕金 森病(有、无) 、鼻饲(是、否) 、急性生理学与 慢性健康状况评分系统Ⅱ(APACHE Ⅱ) [6] 评分、 淋巴细胞计数、中性粒细胞比例、血红蛋白水平、 总胆固醇水平、三酰甘油水平、空腹血糖水平、平 均动脉压、血清超敏 C 反应蛋白(hs-CRP)水平、 血清血管生成素 -2(Ang-2) 水平。APACHE Ⅱ评 分总分 0~71 分,分值越高表示病情越重。面对面 发放问卷,调查者问,患者答,调查者填写,问卷 有效回收率为 100%(150/150)。
1.2.2 预后判定 治疗后 30 d,显效指患者临床症 状、体征完全消失, X 线片显示肺部阴影全部消退, 肺部干湿啰音完全消退;有效为患者临床症状、体 征基本消失,X 线片显示肺部阴影明显减少,肺部干 湿啰音基本消失;无效指患者病情无好转迹象或恶化。 其中显效、有效为预后良好,无效为预后不良。
1.3 观察指标 (1)统计老年 AP 患者预后不良发 生率。(2)比较不同预后患者一般资料。(3)采 用多因素 Logistic 回归分析老年 AP 患者预后的影响因素。
1.4 统计学方法 应用 SPSS 22.0 软件进行统计学分析,计量资料以( x(—) ±s )表示,采用 t 检验,计数资料以率(%)表示,采用 χ2 检验,影响因素分 析采用多因素 Logistic 回归分析,以 P<0.05 为差异 有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 老年 AP 患者预后不良发生率 150 例老年 AP 患者预后不良 41 例, 占 27.33%(41/150); 预后良好 109 例,占 72.67%(109/150)。
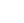
2.2 不同预后患者一般资料比较 预后不良患 者的 APACHE Ⅱ评分、血清 hs-CRP 水平、血清 Ang-2 水平均高于预后良好患者,差异有统计学意 义(P<0.05); 不同预后患者的性别、年龄、BMI、 糖尿病占比、高血压占比、心脑血管疾病占比、帕 金森病占比、鼻饲占比、淋巴细胞计数、中性粒细 胞比例、血红蛋白水平、总胆固醇水平、三酰甘油 水平、空腹血糖水平、平均动脉压比较,差异均无 统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表 1.
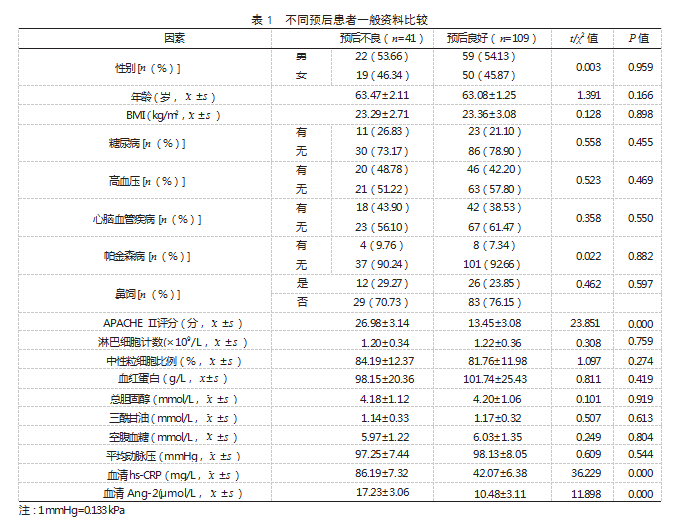
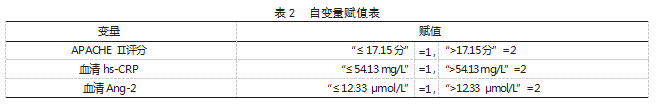
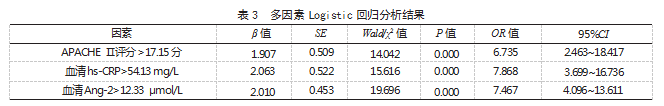
2.3 老年 AP 患者预后影响因素分析 以老年 AP 患者预后情况为因变量(“预后良好”=0. “预 后不良”=1), 多因素 Logistic 回归分析结果显示,APACHE Ⅱ评分 >17.15 分、血清 hs-CRP>54.13 mg/L、 血清 Ang-2>12.33 μmol/L 均为老年 AP 患者预后不 良的危险因素(OR>1. P<0.05)。见表 2、表 3.
3 讨论
AP 根据病因可分为化学性 AP、阻塞性 AP 和 细菌性 AP,患者临床表现为咳嗽、气促、发热等, 严重者可出现呼吸困难, 甚至死亡 [7-8]。探讨 AP 患 者预后的影响因素可为临床治疗提供参考 [9]。
本 研 究多因素 Logistic 回归分析结果显示, APACHE Ⅱ评分 >17.15 分、血清 hs-CRP>54.13 mg/L、 血清 Ang-2>12.33 μmol/L 均为老年 AP 患者预后不 良的危险因素。分析原因:(1)APACHE Ⅱ评分 >17.15 分。APACHE Ⅱ是临床常用于评估危重症患 者病情的量表,其分值越高则病情越严重,预后越 差 [10]。(2) 血清 hs-CRP>54.13 mg/L。血清 hs-CRP 反映全身炎症急性期的非特异性标志物,其水平越 高,机体炎症程度越重,临床治疗难度越大,预后 越差 [11]。(3) 血 清 Ang-2>12.33 μmol/L。Ang-2 对启动炎症反应具有重要作用,且参与肺部氧化损 伤,因此其水平升高可影响预后 [12]。
综 上 所 述,APACHE Ⅱ 评 分 >17.15 分、 血 清 hs-CRP>54.13 mg/L、 血 清 Ang-2>12.33 μmol/L 均为老年 AP 患者预后不良的危险因素。
参考文献
[1] 龙云霞,陈波,姜利琼 . 老年人吸入性肺炎与非吸入性肺炎 的 临 床 特 征及肺 功 能 比 较 [J]. 河 北 医 药,2020.42(11): 1649-1652.1656.
[2] Scannapieco FA.Poor oral health in the etiology and prevention of aspiration pneumonia[J]. Dent Clin North Am,2021. 65(2) : 307-321.
[3] 舒方茂, 宋宁, 张宇 . 吸入性肺炎研究进展 [J]. 国际呼吸杂志, 2020.40(3):215-219.
[4] 张博寒,刘悦,田莉,等 . 老年患者吸入性肺炎防治与管 理的最佳证据总结 [J]. 中华现代护理杂志,2021.27(7): 888-895.
[5] 王蔚文 . 临床疾病诊断与疗效判断标准 [M]. 北京:科学技术 文献出版社,2010:138.
[6] 刘先松,董永书 . 针刺联合吞咽训练对脑卒中后吞咽障碍病 人 SSA 评分、MNA 评分及吸入性肺炎发生率的影响 [J]. 中西 医结合心脑血管病杂志,2021.19(12):2083-2086.
[7] 杨亚丽 . 纤维支气管镜下支气管灌洗结合盐酸氨溴索雾化吸 入治疗老年吸入性肺炎临床效果及不良反应分析 [J]. 中国药 物与临床,2021.21(20):3451-3453.
[8] Teramoto S. The current definition, epidemiology,animal models and a novel therapeutic strategy for aspiration pneumonia[J]. Respir Investig,2022.60(1):45-55.
[9] Khadka S,Khan S,King A, et al. Poor oral hygiene,oral microorganisms and aspiration pneumonia risk in older people in residential aged care: asystematic review[J]. Age Ageing,2021. 50(1):81-87.
[10] Tang W,Zha ML,Zhang WQ, et al. APACHE scoring system and pressure injury risk for intensive care patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Wound Repair Regen,2022.30 (4):498-508.
[11] 孟超,范志强,佟庆,等 . 血清可溶性髓样细胞触发受体 1、 高敏 C 反应蛋白联合急性生理和慢性健康状况评分Ⅱ对肺炎 合并呼吸衰竭患者预后评估的价值 [J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2021.25(21):88-92.
[12] 李朝晖,李复红,韩蓓,等 . 血清 D- 二聚体、降钙素原联合 APACHE Ⅱ评分对老年 SCAP 患者预后的预测价值 [J]. 海南医 学,2020.31(14):1790-1793.