经皮椎体成形术对老年胸腰椎骨折患者的影响论文
2024-06-13 09:23:27 来源: 作者:xieshijia
摘要:目的:探究经皮椎体成形术(PVP)对老年胸腰椎骨折患者的影响。方法:选取2021年1月—2023年2月淮安八十二医院收治的101例老年胸腰椎骨折患者为研究对象。根据随机数表法将其分为观察组(50例)和对照组(51例)。观察组实施PVP,对照组实施保守治疗。比较两组椎体情况、生活质量、并发症。结果:治疗后1个月,两组椎体压缩率降低,观察组椎体压缩率低于对照组,椎体高度恢复度高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。治疗后1个月,两组生命质量测定量表(QLQ-C30)评分均升高,观察组QLQ-C30评分高
【摘要】目的:探究经皮椎体成形术(PVP)对老年胸腰椎骨折患者的影响。方法:选取2021年1月—2023年2月淮安八十二医院收治的101例老年胸腰椎骨折患者为研究对象。根据随机数表法将其分为观察组(50例)和对照组(51例)。观察组实施PVP,对照组实施保守治疗。比较两组椎体情况、生活质量、并发症。结果:治疗后1个月,两组椎体压缩率降低,观察组椎体压缩率低于对照组,椎体高度恢复度高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。治疗后1个月,两组生命质量测定量表(QLQ-C30)评分均升高,观察组QLQ-C30评分高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。观察组并发症发生率低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论:对于老年胸腰椎骨折患者,PVP能够有效地恢复椎体高度,促进患者的康复,改善生活质量,降低并发症发生率。
【关键词】经皮椎体成形术;生活质量;老年胸腰椎骨折;椎体压缩率;椎体高度恢复;并发症
Effect of Percutaneous Vertebroplasty on Elderly Patients with Thoracolu
mbar Fracture/JI Chunbo,HU Xuebin,TONG Kai,ZHANG Qizhu.//Chinese and Foreign Medical Research,2024,22(7):121-124
[Abstract]Objective:To investigate the effect of percutaneous vertebroplasty(PVP)on elderly patients with thoracolumbar fracture.Method:A total of 101 elderly patients with thoracolumbar fracture admitted to the Huai’an Eighty-two Hospital from January 2021 to February 2023 were selected as the study objects.They were divided into observation group(50 cases)and control group(51 cases)according to random number table method.The observation group received PVP and the control group received conservative treatment.The vertebral body condition,quality of life and complications were compared between the two groups.Result:One month after treatment,the vertebral compression rate decreased in the two groups,the vertebral compression rate in the observation group was lower than that in the control group,and the vertebral height recovery degree was higher than that in the control group,the differences were statistically significant(P<0.05).One month after treatment,the quality of life questionnaire core-30(QLQ-C30)scores of both groups were increased,and the QLQ-C30 score of the observation group was higher than that of the control group,the differences were statistically significant(P<0.05).The incidence of complications in the observation group was lower than that in the control group,the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05).Conclusion:For elderly patients with thoracolumbar fracture,PVP can effectively restore the vertebral height,promote the rehabilitation of patients,improve the quality of life and reduce the incidence of complications.
[Key words]Percutaneous vertebroplasty Quality of life Elderly thoracolumbar fractures Vertebral compression rate Vertebral height recovery Complications
First-author's address:Huai’an Eighty-two Hospital,Huai’an 223001,China
胸腰椎骨折是一种常见的脊柱损伤,其损伤机制和并发症相当复杂,因此在诊断和治疗方面具有很高的难度。对于胸段和腰段的骨折,医生可以根据解剖结构的特点进行划分。由于人口老龄化程度不断加剧,老年胸腰椎骨折的病例数量也在逐年增加。对于椎体骨折,尤其是存在裂缝的中央骨折,可以采用手术或非手术治疗方法[1-7]。目前临床上常用手术对老年胸腰椎骨折进行治疗,有研究表明,经皮椎体成形术(PVP)能够缓解疼痛,效果优于常规保守治疗[8]。因此,本研究选取101例老年胸腰椎骨折患者,探讨上述问题,现报道如下。
1资料与方法
1.1一般资料
选取2021年1月—2023年2月淮安八十二医院收治的101例老年胸腰椎骨折患者为研究对象。纳入标准:符合老年胸腰椎骨折的诊断[9];均符合PVP手术指征;年龄60~91岁。排除标准:恶性肿瘤;伴有心血管及血液系统疾病;意识不清晰;患有免疫缺陷。根据随机数表法将其分为观察组(50例)和对照组(51例)。观察组男13例,女37例;年龄65~71岁,平均年龄(68.52±1.24)岁;胸椎30例,腰椎20例。对照组男10例,女41例;年龄66~70岁,平均年龄(69.36±1.01)岁;胸椎32例,腰椎19例。两组一般资料比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),有可比性。本研究经医院医学伦理委员会批准,患者或患者家属均签署知情同意书。
1.2方法
观察组实施PVP,对照组实施保守治疗。
保守治疗:(1)卧床休息。在初始阶段,患者需要卧床休息,以减少脊柱负荷,促进骨折部位的愈合。床垫应选择硬度适中的床垫。(2)疼痛管理。对于疼痛较重的患者,可以进行疼痛管理,包括非处方镇痛药物(如对乙酰氨基酚)或处方镇痛药物。必要时,可以使用骨密度增加药物或具有骨形成作用的药物来促进骨折愈合。(3)硬件支持。严重骨折存在椎体塌陷的患者,需要使用背夹、腰带或其他支具来提供稳定性和支持,减轻疼痛并促进骨折愈合。(4)物理治疗。在医生指导下进行物理治疗,如肌肉强化运动、康复训练等,可以帮助提高患者的日常功能和生活质量。(5)饮食调理。合理饮食对于骨折愈合非常重要,患者应摄入足够的钙、维生素D和蛋白质,以促进骨组织的修复和再生。(6)密切随访。定期复诊,密切观察骨折部位的愈合情况,调整治疗方案,并及时处理并发症或其他问题。
PVP:(1)穿刺。首先在椎体附近麻醉患者皮肤,然后在合适的位置进行穿刺。通常穿刺点位选择在椎体的上下缘之间。(2)椎体成型。将聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯(PMMA)等填充物质注入,填补椎体空洞,以使椎体得到支撑,缓解患者的疼痛,同时恢复椎体形态和稳定性。注意填充物质的注射量,应根据椎体的具体情况和患者的身体状况进行个性化评估。(3)结束手术。填充物注入完成后,医生拔除扩张器和穿刺针,对穿刺部位进行止血和消毒处理,结束手术。
1.3观察指标及评价标准
(1)椎体情况:比较两组治疗前、治疗后1个月椎体情况。包括椎体压缩率及椎体高度恢复度。椎体压缩率:记录患者治疗后椎体压缩率[通过X射线、磁共振成像(MRI)或计算机断层扫描(CT)等影像学检查来获取]、椎体高度恢复度(将治疗前后的椎体高度进行比较,通过计算椎体高度的差异来评估椎体高度恢复度)。(2)生活质量:比较两组治疗前和治疗后1个月生活质量。采用生命质量测定量表(QLQ-C30)评价,包括社会、认知、躯体、角色和情绪5个方面,总分为100分,得分越高表示患者生活质量越好[10]。(3)并发症:比较两组并发症。包括脊髓损伤、压疮、神经根痛。
1.4统计学处理
本研究数据采用SPSS 21.0统计学软件进行分析和处理,符合正态分布计量资料以(x-±s)表示,采用t检验,计数资料以率(%)表示,采用χ2检验,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2结果
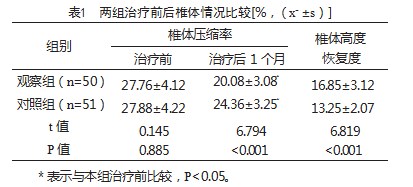
2.1两组治疗前后椎体情况比较
治疗前,两组椎体压缩率比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);治疗后1个月,两组椎体压缩率降低,观察组椎体压缩率低于对照组,椎体高度恢复度高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),见表1。
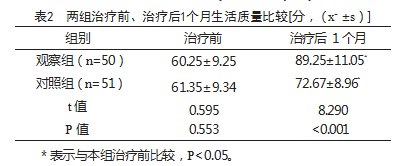
2.2两组治疗前、治疗后1个月生活质量比较
治疗前,两组QLQ-C30评分比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);治疗后1个月,两组QLQ-C30评分均升高,观察组QLQ-C30评分高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),见表2。
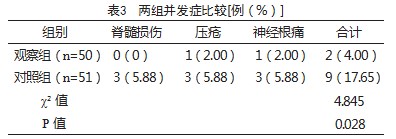
2.3两组并发症比较
观察组并发症发生率低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),见表3。
3讨论
胸腰椎骨折是老年人常见的骨折类型之一,由于骨质疏松和肌力减退等因素,老年患者的骨折愈合和康复过程较为困难[11-12]。PVP作为一种微创手术技术,在目前骨折治疗中运用广泛[13-14]。然而,PVP手术对于老年胸腰椎骨折患者脊柱功能和生活质量的影响尚需开展研究。本文旨在系统研究PVP对老年胸腰椎骨折患者的影响,并提供一份证据支持。
本研究发现,治疗后1个月,两组椎体压缩率降低,观察组椎体压缩率低于对照组,椎体高度恢复度高于对照组,提示对于老年胸腰椎骨折患者,PVP能够有效恢复椎体高度,降低椎体压缩率。PVP虽然是一种介入治疗胸腰椎骨折的方法,但是它主要用于减轻疼痛和改善功能。在PVP治疗过程中,医生通过向椎体内注入PMMA等填充物质来达到减轻疼痛和恢复功能的目的。填充物主要起到填补椎体空洞的作用,以使椎体得到支撑,缓解患者的疼痛。PVP通过注射PMMA等固定物质可以恢复椎体高度、稳定椎体结构和增加椎体的抗压能力,在一定程度上能够改善骨折,并减少椎体的压缩率[15-16]。
本研究还发现,治疗后1个月,两组QLQ-C30评分均升高,观察组QLQ-C30评分高于对照组,提示对于老年胸腰椎骨折患者,PVP能够改善患者的生活质量。PVP能够填补椎体空洞,使椎体得到支撑,缓解患者的疼痛,同时恢复椎体形态和稳定性。随着疼痛减轻和功能恢复,患者的身体状态会有所改善,例如体力逐渐增强、睡眠质量提高、心理状态得到缓解等,这些都与患者的生活质量密切相关。此外,PVP手术创伤较小,恢复较快,患者可以早期进行康复训练,促进身体的康复[17-20]。此外,观察组并发症发生率低于对照组,提示PVP治疗老年胸腰椎骨折,可降低并发症发生率。
综上所述,对于老年胸腰椎骨折患者,PVP能够有效恢复椎体高度,促进患者恢复,改善患者的生活质量,降低并发症发生率。
参考文献
[1]TANG J,GUO W C,HU J F,et al.Unilateral and bilateral percutaneous kyphoplasty for thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fractures[J].J Coll Physicians Surg Pak,2019,29(10):946-950.
[2]BURT L A,BILLINGTON E O,ROSE M S,et al.Effect of high-dose Vitamin D supplementation on volumetric bone density and bone strength:a randomized clinical trial[J].JAMA,2019,322(8):736-745.
[3]ZHANG J,ZHANG T,XU X,et al.Zoledronic Acid combined with percutaneous kyphoplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic compression fracture in a single T 12 or L1 vertebral body in postmenopausal women[J].Osteoporos Int,2019,30(7):1475-1480.
[4]FUGGLE N R,CURTIS E M,WARD K A,et al.Fracture prediction,imaging and screening in osteoporosis[J].Nat Rev Endocrinol,2019,15(9):535-547.
[5]REPO J P,PONKILAINEN V T,HÄKKINEN A H,et al.Assessment of construct validity of the oswestry disability index and the scoliosis research society-30 questionnaire(SRS-30)in patients with degenerative spinal disease[J].Spine Deform,2019,7(6):929-936.
[6]林岿然.椎体内裂隙位置对PVP手术疗效的影响[J].颈腰痛杂志,2018,39(5):14-17.
[7]YONEZAWA N,TOKUUMI Y,KOMINE N,et al.Simultaneous-onset infectious spondylitis with vertebral fracture mimicking an acute osteoporotic vertebral fracture erroneously treated with balloon kyphoplasty:illustrative case[J].Journal of Neurosurgery,2021,2(12):17.
[8]AN N,LIN J,FEI Q.Beijing friendship hospital osteoporosis self-assessment tool for elderly male(BFH-OSTM)vs fracture risk assessment tool(FRAX)for identifying painful new osteoporotic vertebral fractures in older Chinese men:across-sectional study[J].BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders,2021,22(1):17.
[9]TERAI H,TAKAHASHI S,YASUDA H,et al.Differences in surgical outcome after anterior corpectomy and reconstruction with an expandable cage with rectangular footplates between thoracolumbarand lumbar osteoporotic vertebral fracture[J].North American Spine Society Journal(NASSJ),2021,6(7):96.
[10]邱彩锋.QLQ-C30的应用及计分方法[J].国外医学.护理学分册,2005,4(11):53-55.
[11]MAO S,LI D,AHMAD K.Ability of assessing osteoporosis and osteoporotic vertebral fracture in the general population when using thoracic quantitative computed tomography:a comparison study between low-dose thoracic quantitative computed tomography and lumbar dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry[J].Journal of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography,2021,15(4):85.
[12]MORISHITA S,YOSHII T,OKAWA A,et al.Risk factors related to perioperative systemic complications and mortality in elderly patients with osteoporotic vertebral fractures-analysis of a large national inpatient database[J].Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research,2020,15(1):41.
[13]ORTIN-BARCELO A,ORTOLÀMORALES D J,ROSA M A,et al.Adjacent single-level combined fixation using kyphoplasty and percutaneous pedicle screws in type A3 unstable vertebral fractures in elderly patients[J].Folia Med(Plovdiv),2018,60(3):474-478.
[14]GAO C,ZONG M,WANG W T,et al.Analysis of risk factors causing short-term cement leakages and long-term complications after percutaneous kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures[J].Acta Radiol,2018,59(5):577-585.
[15]FRANKLIN D B 3RD,HARDAWAY A T,SHEFFER B W,et al.The role of computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of pediatric thoracolumbar compression fractures[J/OL].J Pediatr Orthop,2019,39(7):e520-e523.
[16]严越茂,李世平,肖建斌.经皮椎体成形术治疗老年创伤性胸腰椎骨折的临床研究[J].赣南医学院学报,2022,42(2):167-169,193.
[17]张国平,史舅生,靳兆印.经皮椎体成形术治疗老年骨质疏松性胸腰椎骨折治疗后并发迟发性后凸畸形危险因素分析[J].创伤外科杂志,2021,23(12):891-895.
[18]陈杰,高兵.高黏度骨水泥经皮椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性胸腰椎骨折的临床效果[J].中外医学研究,2021,19(31):132-134.
[19]BAE J W,GWAK H S,KIM S,et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty for patients with metastatic compression fractures of the thoracolumbar spine:clinical and radiological factors affecting functional outcomes[J].Spine J,2016,16(3):355-364.
[20]张涛.经皮椎体成形术联合阿仑膦酸钠治疗骨质疏松性胸腰椎骨折的效果及对患者预后的影响[J].中国医学创新,2022,19(28):77-80.